Kratom's Active Compounds: A Scientific Analysis
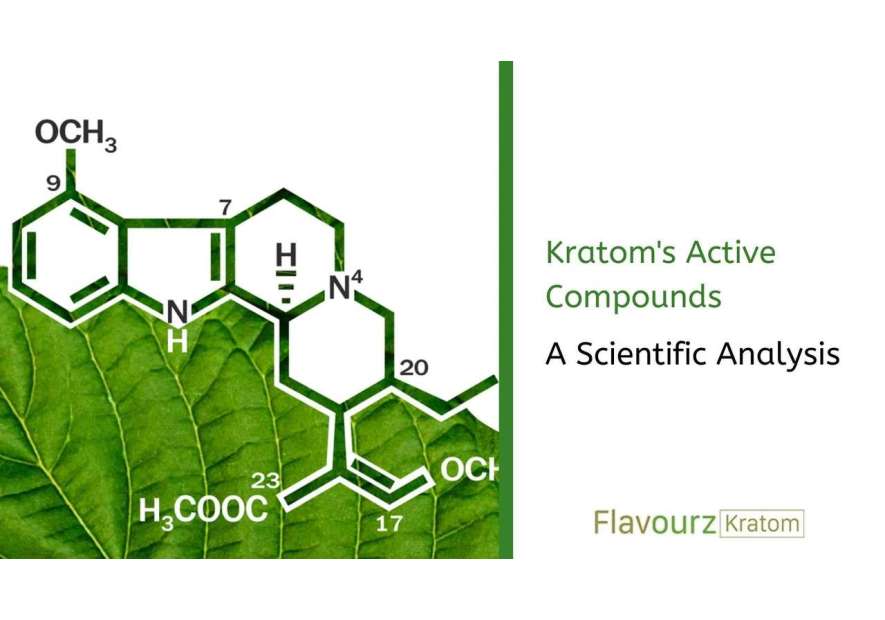
Kratom is a tropical tree (Mitragyna speciosa) native to Southeast Asia whose leaves contain alkaloids like mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine that interact with the body's opioid receptors. According to NIDA, kratom can produce both opioid-like and stimulant-like effects, but carries significant health risks and has not been approved by the FDA for any medical use.
With 25 years of experience serving over 10,000 customers at Flavourz Kratom, we emphasize that understanding kratom's compounds, effects, and risks is essential for anyone considering its use.
| Alkaloid | Percentage | Primary Effects | Receptor Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitragynine | 60-66% | Mood, focus, mild stimulation | Partial μ-opioid agonist |
| 7-Hydroxymitragynine | ~2% | Relaxation, pain relief | Strong μ-opioid agonist |
| Paynantheine | 8-9% | Muscle relaxation | Opioid antagonist |
| Speciogynine | ~6% | Relaxation, pain relief | Opioid receptor activity |
Important Safety Warning: Kratom has not been evaluated by the FDA and carries serious health risks including dependency, dangerous drug interactions, and potential liver damage. The DEA lists kratom as a Drug and Chemical of Concern. Always consult healthcare professionals before use.
Kratom, scientifically known as Mitragyna speciosa, is a tropical tree from the coffee family (Rubiaceae). Kratom alkaloids contain mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, which influence how kratom works in the body.
This plant has a history dating back centuries in Southeast Asia, where Indigenous cultures have used it traditionally. However, modern scientific understanding reveals significant safety concerns.
The primary compounds in kratom are called indole alkaloids. These interact with your μ-opioid receptors and act as partial agonists, creating various effects that can influence mood and provide stimulation or relaxation depending on dose.
What Are Kratom Active Compounds
Kratom contains over 40 alkaloids, but the main active compounds are: Mitragynine, the most abundant alkaloid responsible for most effects, and 7-hydroxymitragynine, a more potent alkaloid found in smaller amounts. Research from Nature Scientific Reports shows these alkaloids have distinct receptor binding profiles.
Other active compounds include indole alkaloids such as paynantheine, speciociliatine, and speciogynine that also contribute to kratom's overall effects. These alkaloids interact with neurotransmitters and opioid receptors, influencing kratom's various effects.
In my 5+ years working with kratom customers at Flavourz, I've learned that understanding these compounds helps users make more informed decisions about kratom use. However, it's crucial to understand that even natural compounds can be dangerous.
Explore green malay kratom for sale to experience its active compounds.
What Is The Historical Use of Kratom?
Traditionally, kratom was used mainly by farmers in Southeast Asia. It was either chewed or brewed into tea, allowing the gradual release of its chemical compounds.
This helped with their work, providing energy and relief from discomfort. In some regions, kratom was used during cultural practices and passed down through generations.
The history of kratom dates back many centuries. It comes from Southeast Asia, where it has been part of culture and traditional practices.
Indigenous communities in Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia have used kratom (Mitragyna Speciosa) for centuries. However, traditional use doesn't guarantee safety, and many countries have now banned or restricted kratom due to health concerns.
As kratom spread to other parts of the world like the United States, products like kratom extracts, kratom capsules, and kratom tinctures became more available. With its global reach, debate emerged about safety and regulation.
'Ketum' is the local name for 'kratom' in Malaysia. Understanding kratom's origins is important when studying it.
However, as modern interest in kratom's chemistry grows, the potential health risks and lack of FDA approval are necessary conversations for understanding the product safely.
Check out red bali kratom for sale to learn about its unique properties.
Alkaloids and Their Role in Kratom's Effects
Kratom (Mitragyna Speciosa) contains over 40 different alkaloid compounds. A few key compounds play important roles in kratom's mechanism of action and overall effects.
Interacting with body receptors causes kratom's effects, but also its risks. Some of these kratom alkaloids are:
1. Mitragynine: This compound is the most abundant alkaloid, making up 60-66% of alkaloid content. It acts as a partial agonist at μ-opioid receptors, allowing it to influence receptors but not activate them as strongly as other substances.
Mitragynine also influences other receptors such as adrenergic, serotonergic, and dopamine receptors. This may contribute to mood and focus-related effects.
What are the basic effects of kratom? Mitragynine plays a significant role in kratom's effects and overall activity.
2. 7-Hydroxymitragynine: Also known as 7-OH, this compound has only 2% alkaloid content. However, it is essential in kratom's pain-relieving effects by strongly activating opioid receptors.
Due to its high affinity, it reacts strongly even in small dosages. This compound contributes to kratom's potential for dependency and abuse.
3. Paynantheine: With about 8-9% of total alkaloids, Paynantheine acts as an opioid receptor antagonist. It functions as a muscle relaxant, contributing to kratom's overall effects.
Although it's not studied as much as 7-OH and mitragynine, it plays a role in kratom's complex effects.
4. Speciociliatine: This alkaloid makes up less than 1% of kratom's alkaloid content. It has weak binding affinity and weakly influences the neurotransmitter system.
However, it acts as a stereoisomer of mitragynine, meaning it has similar molecular structure but different spatial arrangement.
5. Speciogynine: Influencing kratom's effects like pain relief and relaxation, Speciogynine is an abundant alkaloid. It is similar to Paynantheine but has only 6% of alkaloid content.
By understanding kratom chemistry and how its alkaloids interact with the body, consumers can make informed choices about various kratom extracts and their potential risks. As research continues, more insights into kratom alkaloid effects emerge, shaping the conversation around its safety and regulation.
Based on our 25 years of experience serving customers, we strongly emphasize that this research reveals both potential benefits and serious risks that users must understand.
Discover white borneo kratom effects in this scientific analysis.
Forms Of Kratom
Kratom comes in diverse forms, each designed to cater to different user needs and lifestyles. From traditional to more modern extracts, kratom products are made to meet various preferences.
Each form is processed with different amounts of alkaloid content, some more potent than others. This ensures that users can find a product that works for their specific needs, though all forms carry risks.
The forms of kratom products include:
1. Kratom Powder: The most traditional way of taking kratom, made from drying kratom leaves and grinding them into powder. This form preserves the plant's natural alkaloid profile.
It is economical and can be used in drinks and tea. Its effects are typically milder than kratom extracts.
2. Kratom Capsules: For users who prefer a pre-measured dose and convenient option, kratom capsules offer these benefits. Capsules allow you to experience alkaloid effects without enduring kratom's bitter taste.
3. Kratom Extracts: Experienced users often prefer this more potent form of kratom. This form is concentrated, made by boiling and filtering kratom leaves to focus mainly on active alkaloids.
This process creates a more potent kratom product with increased risk of side effects and dependency.
4. Kratom Tincture: This form provides a convenient and modern way of using kratom. It is a liquid extract created for easier use.
This tincture contains a concentrated dose of mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, preferred by those who want a pre-measured liquid form. The potency level depends on the extraction method.
5. Kratom Resin: Made from reducing liquid extracts until they become dense. This tar-like substance, due to its production method, is a highly concentrated form of the plant's active compounds.
Each of these kratom products offers a distinct way to experience kratom's alkaloid effects, whether through traditional brewing methods or modern extracts. Understanding these different forms allows consumers to choose options based on their preferences and desired effects when buying kratom products.
However, all forms carry risks including potential dependency, side effects, and drug interactions that users must understand before use.
What Is a Kratom Psychonaut?
Kratom Psychonauts are people who are interested in kratom and how alkaloids interact with opioid receptors as partial agonists. The word "Psychonaut" refers to people who explore altered states of consciousness, often through experience and study of plants like kratom.
They usually research kratom's origin, the kratom mechanism of action, and its growth in the United States. To understand kratom tinctures, capsules, and extracts, they conduct studies to determine how different preparations influence kratom effects.
However, the psychonaut community should emphasize responsible exploration—understanding kratom alkaloid effects, potential side effects, and dangerous drug interactions is critical for safety. As scientific curiosity around kratom chemistry grows, kratom psychonauts must prioritize safety and legal considerations.
How Do Kratom Alkaloids Work In The Body?
Once consumed, kratom's alkaloids are absorbed into the bloodstream, where they bind to opioid receptors, particularly the μ-opioid receptors. However, unlike full opioid agonists, alkaloids activate receptors to varying degrees.
This contributes to kratom's distinct effects but also its potential for dependency and abuse.
Additionally, alkaloids interact with other neurotransmitter systems, including:
- Adrenergic receptors: influence energy levels and focus.
- Serotonergic receptors: which may contribute to mood-related effects.
- Dopaminergic receptors: play a role in motivation and pleasure responses.
The liver then breaks down mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine into metabolites, which continue to interact with the body's receptors. These metabolites influence the effects of kratom, which can differ based on factors like dosage, strain, and individual body chemistry.
This is why kratom's impact can vary significantly from person to person. It also explains why some people may experience serious adverse effects or develop dependency.
Different kratom products, such as kratom tinctures or kratom extracts, may affect each individual differently and carry varying risk profiles.
What Is The Difference Between Ketum And Kratom?
There is no difference between Ketum and Kratom. They both refer to the same plant (Mitragyna speciosa).
Locally in Malaysia, "kratom" is called Ketum. However, as it spread to the United States, it became known as kratom.
Ultimately, Ketum and kratom are the same plant; the only difference is the name and regional terminology.
Is Kratom Legal In The United States?
Kratom legality varies by state as of September 2025. Although federal laws don't ban the buying and selling of kratom, some states have placed regulations or complete bans.
Regulatory agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and DEA monitor kratom, raising concerns about its alkaloid effects and potential adverse health effects. The FDA has issued warnings about kratom's safety and has not approved it for any medical use.
Some states where kratom is currently banned or restricted include Alabama, Arkansas, Indiana, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Wisconsin. Always check your local and state laws before purchasing or using kratom.
Can Kratom Interact With Other Substances?
Yes, kratom can interact dangerously with other substances. Understanding drug interactions is vital for safe use and can be life-threatening.
Users need to understand that kratom interacting with other substances can lead to severe adverse effects and unpredictable reactions. We strongly advise proper medical consultation and avoiding mixing kratom with other drugs or medications.
Kratom can interact with prescription medications, alcohol, and other substances in ways that may increase the risk of respiratory depression, liver damage, or other serious health complications. Never mix kratom with other drugs without medical supervision.
Based on our 25 years of experience, we've seen the importance of understanding these risks and always recommend consulting healthcare professionals before using kratom, especially for those taking medications or with health conditions.
Find trusted powder at Flavourz kratom and buy kratom powder.
Last updated: September 2025. This information is for educational purposes and has not been evaluated by the FDA. Kratom carries significant health risks including potential dependency, liver damage, respiratory depression, and dangerous drug interactions. Individual results may vary greatly. Always consult healthcare professionals before using kratom, especially if you have medical conditions or take medications. Kratom is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease and is listed by the DEA as a Drug and Chemical of Concern.



Leave a comment